Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) is a member of the family Leguminosae. The chickpea has the ability to fix a portion of its nitrogen requirements from air in the soil. The growth habit is erect, with most of the pods formed in the top part of the plant.
Chickpea characteristics
Seed size, shape and colour are variable, but typically the seed is beaked and wrinkled or ribbed. The beak is the protruding seedling root tip.
There are two commercial classes of chickpea:
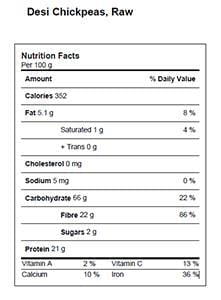
- Desi - The desi type has a thick, coloured seed coat and coloured flowers. It has a long history of production in the Indian subcontinent, and is split and/or milled to make food products.
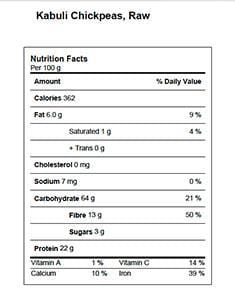
- Kabuli - The kabuli type (also known as garbanzo bean) has a thin, white seed coat and white flowers. It is used mainly in salad and vegetable mixes.
Chickpea plants range from 30-70 cm (12 - 28 in.) in height. Most chickpea varieties have leaves about five cm (two in.) long with nine to fifteen leaflets, and are described as having a fern-leaf structure. Some kabuli varieties have a single (unifoliate) leaf structure instead of leaflets.
Chickpea pods are short and inflated, and contain one or two seeds. The bushel weight of chickpea is 60 lb.
Nutritional Information
Table 1. Nutrient Profile of chickpea
Next: Adaptation and Varieties